Granulomatous Lymphocytic Interstitial Lung Disease
Granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease. A spectrum of pulmonary histopathologic lesions in common variable immunodeficiency--histologic and immunohistochemical analyses of 16 cases. Common variable immunodeficiency is a primary immunodeficiency of unknown etiology characterized by low serum immunoglobulin G a decreased ability to make specific antibodies and. Granulomatous and lymphocytic interstitial lung disease.
Otolaryngology-Head Neck SurgeryAudiology. The granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease GLILD associated with CVID as discussed in this review offers both a promise and challenge. Mohini Pathria Daniel Urbine Marc Stuart Zumberg Juan Guarderas.
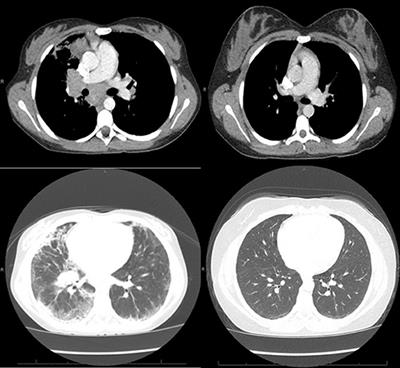
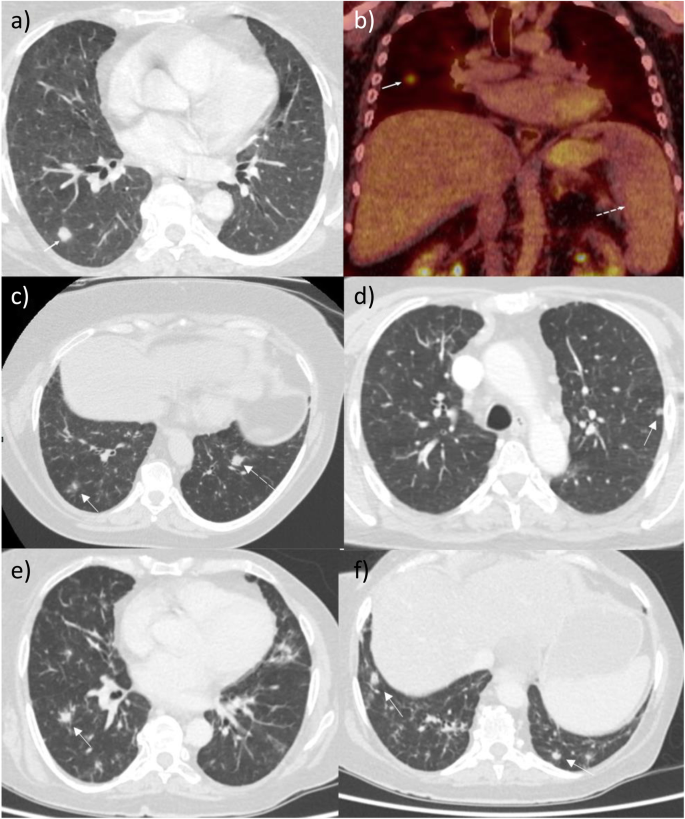
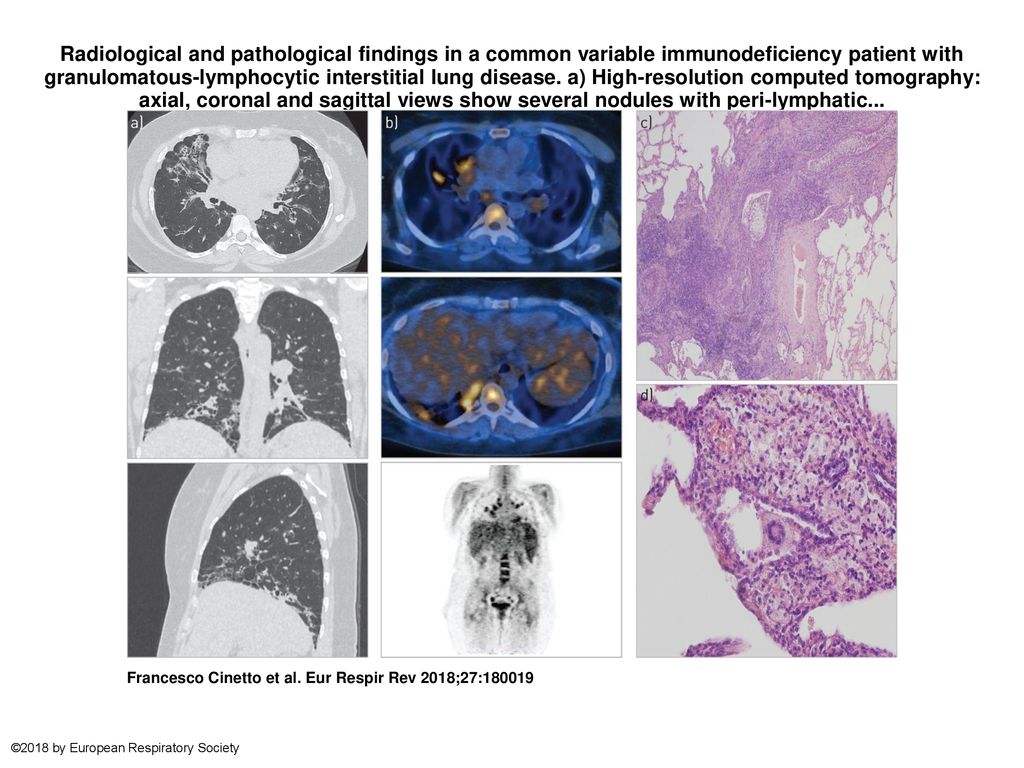
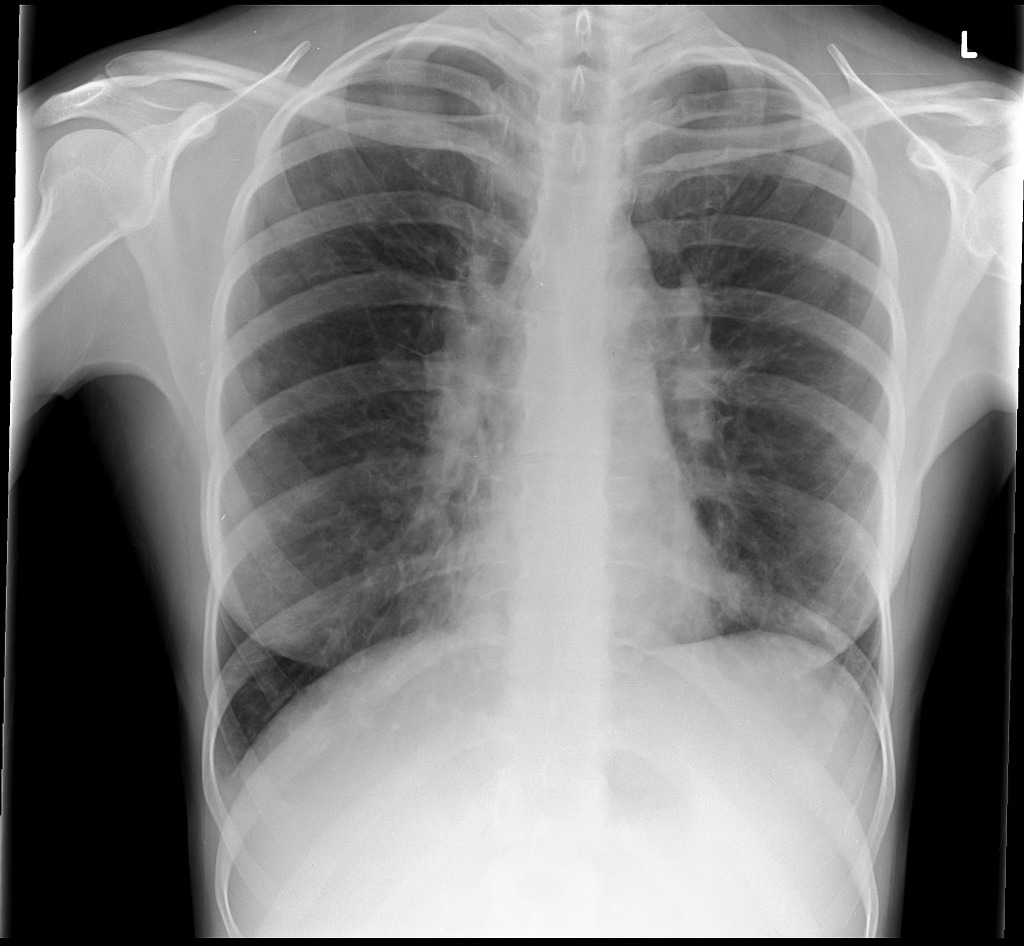
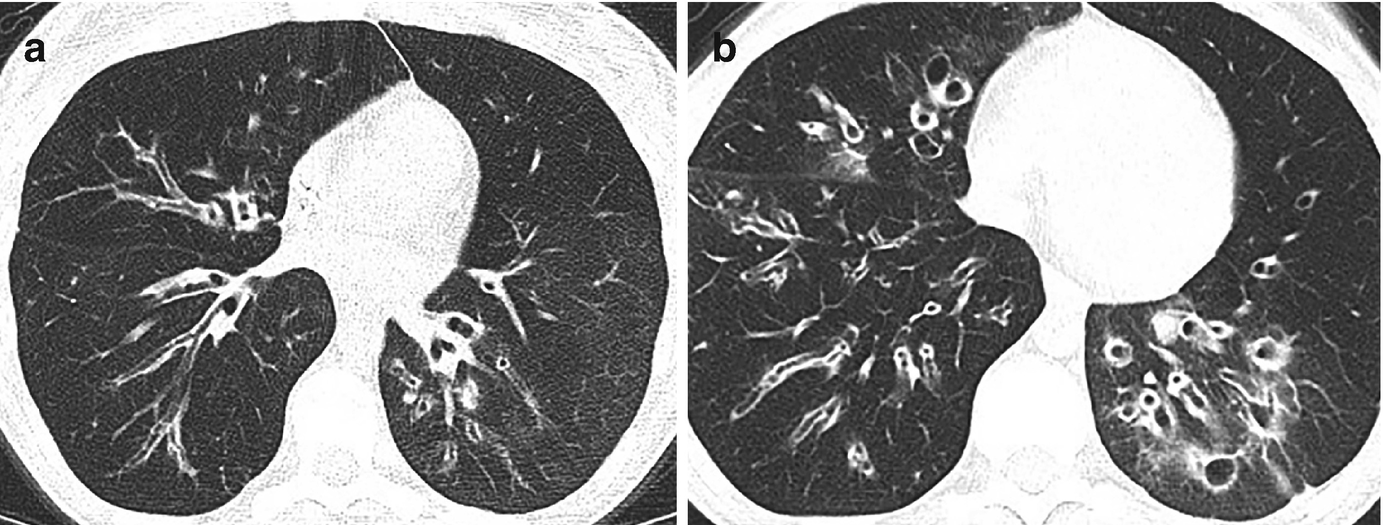
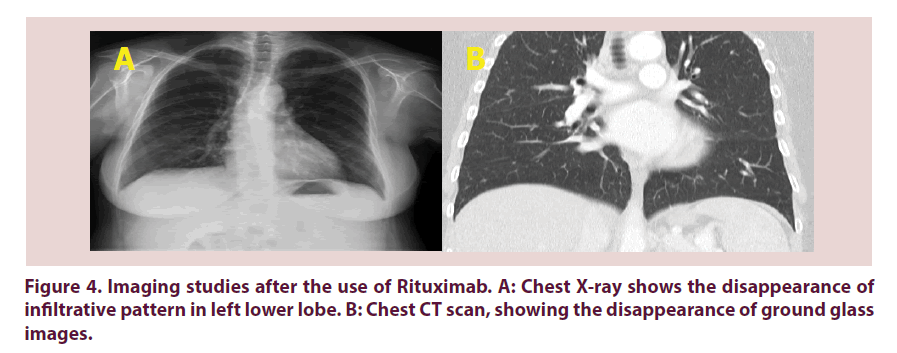
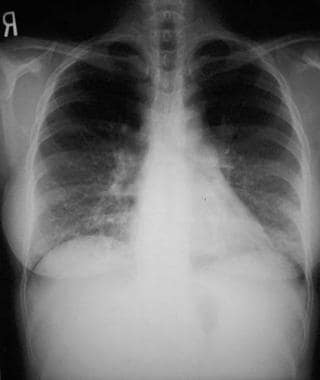
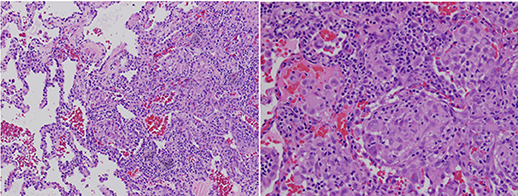
Common variable immunodeficiency CVID is a primary immunodeficiency characterised by B-lymphocyte dysfunction and hypogammaglobulinaemia. Granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease GLILD is characterized by lymphocytic and granulomatous pulmonary infiltration occurring in common variable immunodeficiency CVID. They categorized a group of CVID patients as having GLILD after histological findings in lung biopsies that included granulomas lymphoid interstitial pneumonitis lymphoid hyperplasia and follicular bronchiolitis.
It is associated with increased mortality. Granulomatouslymphocytic interstitial lung disease. The immunological data of.
This relatively unstudied pathologic entity sheds an important light on revealing noninfectious pulmonary complications occurring. Granulomatous Lymphocytic Interstitial Lung Disease GLILD is an inflammatory pulmonary complication of common variable immunodeficiency CVID with distinctive patterns in the biopsy. Granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease GLILD is characterized by lymphocytic and granulomatous pulmonary infiltration occurring in common variable immunodeficiency CVID.
Granulomatous disease lymphocytic interstitial disease follicular bronchiolitis and areas of organizing pneumonia 12. It is associated with increased mortality compared with CVID patients without GLILD. Granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease GLILD is a diffuse lung disease characterized by both granulomatous and lymphoproliferative histopathologic patterns in the lung.
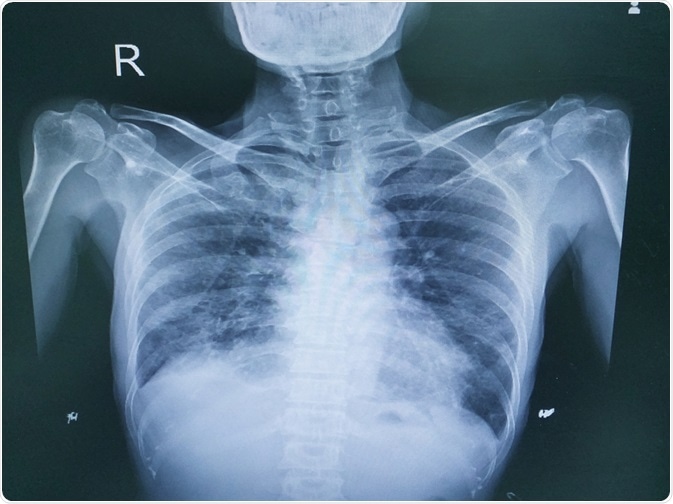
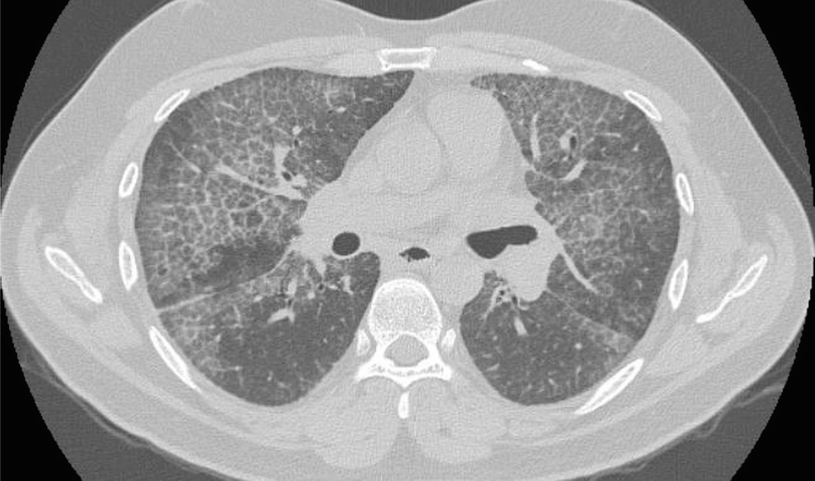
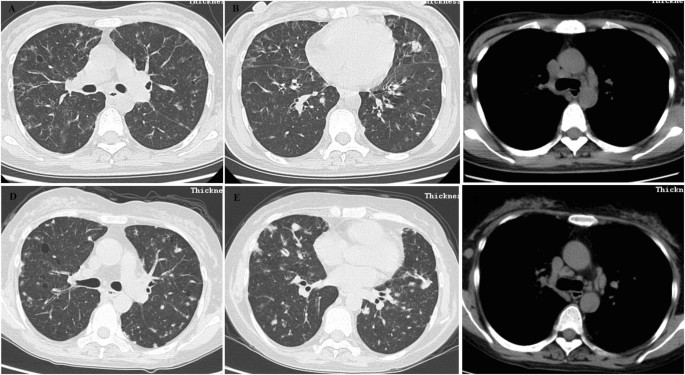
Sarcoidosis a form of interstitial lung disease is a rare disease characterized by the discrete accumulation of inflammatory cells and matrix proteins granulomas in different parts of the body typically the lungs pulmonary sarcoidosis. Granulomatouslymphocytic interstitial lung disease GLILD is a rare potentially severe pulmonary complication of common variable immunodeficiency disorders CVID.
Common variable immunodeficiency CVID is a primary immunodeficiency characterised by B-lymphocyte dysfunction and hypogammaglobulinaemia.
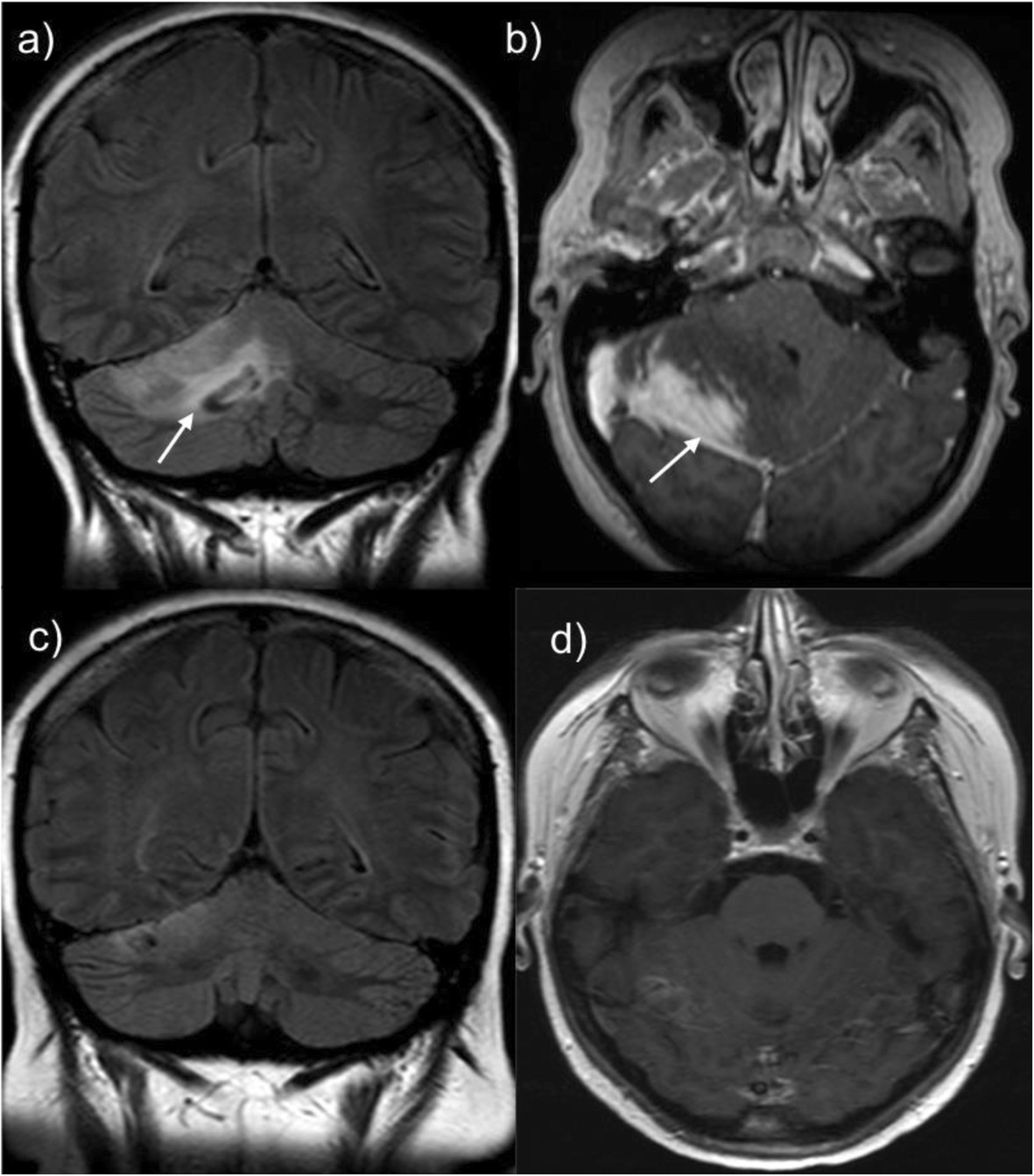
Granulomatous and lymphoproliferative inflammation sometimes affects small airways and the pulmonary interstitium this is termed granulomatouslymphocytic. It is associated with increased mortality compared with CVID patients without GLILD. Granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease as the first manifestation of common variable immunodeficiency. Common variable immunodeficiency CVID is a primary immunodeficiency characterised by B-lymphocyte dysfunction and hypogammaglobulinaemia. Granulomatouslymphocytic interstitial lung disease GLILD is a rare potentially severe pulmonary complication of common variable immunodeficiency disorders CVID. The immunological data of. Learn more about interstitial lung disease ILD. Otolaryngology-Head Neck SurgeryAudiology. Granulomatous disease lymphocytic interstitial disease follicular bronchiolitis and areas of organizing pneumonia 12.
Granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease GLILD is characterized by lymphocytic and granulomatous pulmonary infiltration occurring in common variable immunodeficiency CVID. Although GLILD was classically identified as a non-infectious complication of common variable immunodeficiency CVID it is now being recognized in other primary immunodeficiency disorders 6. They categorized a group of CVID patients as having GLILD after histological findings in lung biopsies that included granulomas lymphoid interstitial pneumonitis lymphoid hyperplasia and follicular bronchiolitis. Granulomatous-lymphocytic interstitial lung disease GLILD is a diffuse lung disease characterized by both granulomatous and lymphoproliferative histopathologic patterns in the lung. Granulomatous disease lymphocytic interstitial disease follicular bronchiolitis and areas of organizing pneumonia 12. Granulomatous and lymphoproliferative inflammation sometimes affects small airways and the pulmonary interstitium this is termed granulomatouslymphocytic. This relatively unstudied pathologic entity sheds an important light on revealing noninfectious pulmonary complications occurring.






























Post a Comment for "Granulomatous Lymphocytic Interstitial Lung Disease"